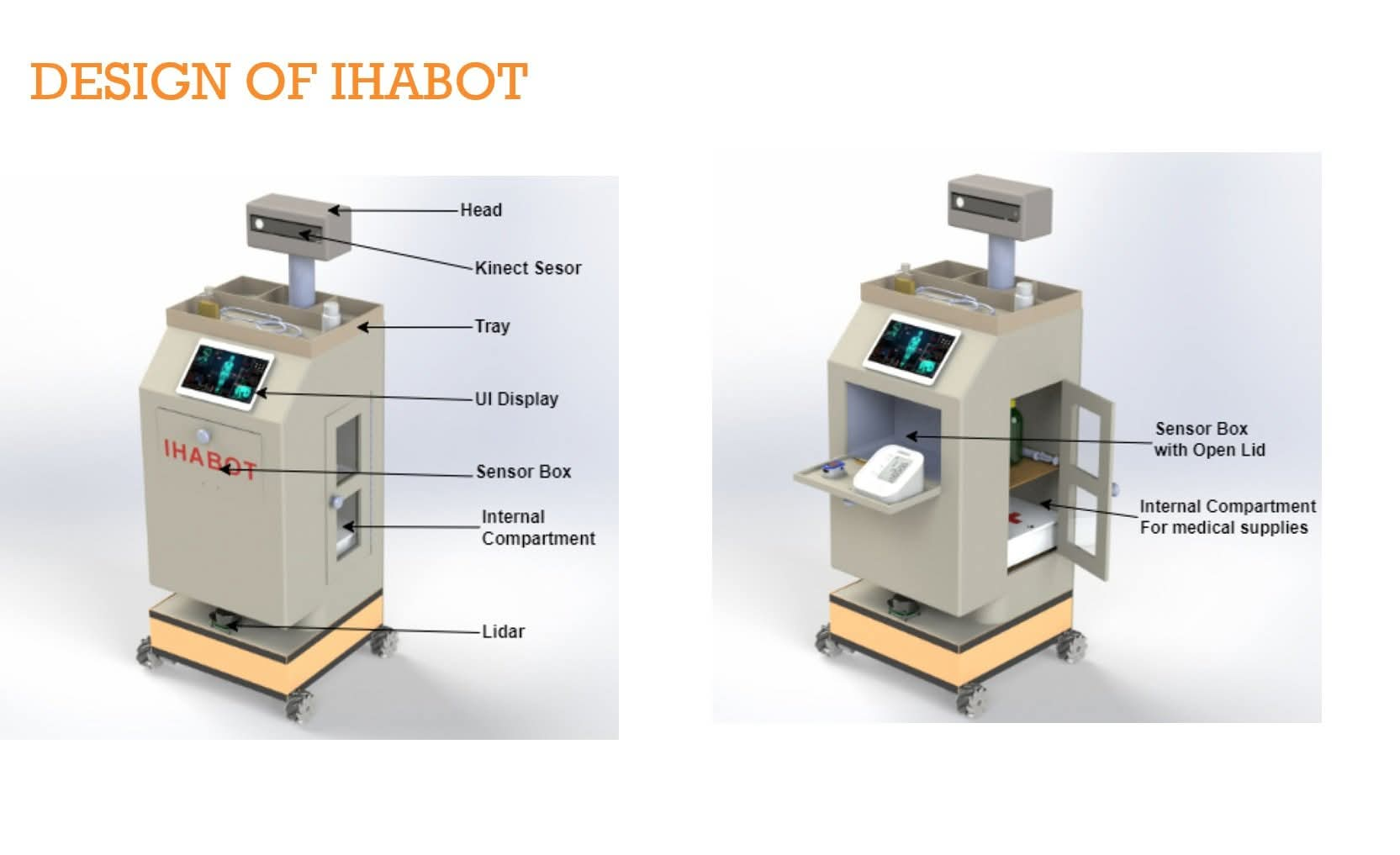
IHABOT — Intelligent Hospital Assistance Robot
Autonomous medical assistive robot developed to minimize direct doctor–patient contact in hospital environments during contagious disease outbreaks
Objective
The objective of this project was to design and develop an autonomous medical assistive robot capable of safe and reliable operation in hospital environments, with the goal of minimizing direct doctor–patient contact during contagious disease outbreaks. Emphasis was placed on robust autonomous navigation, system reliability in real-world clinical settings, and practical deployment to support healthcare professionals while reducing the risk of disease transmission.
My role
- Led autonomous navigation stack development
- Implemented navigation + perception for indoor medical environments
- Integrated health-monitoring sensors for real-time patient data acquisition
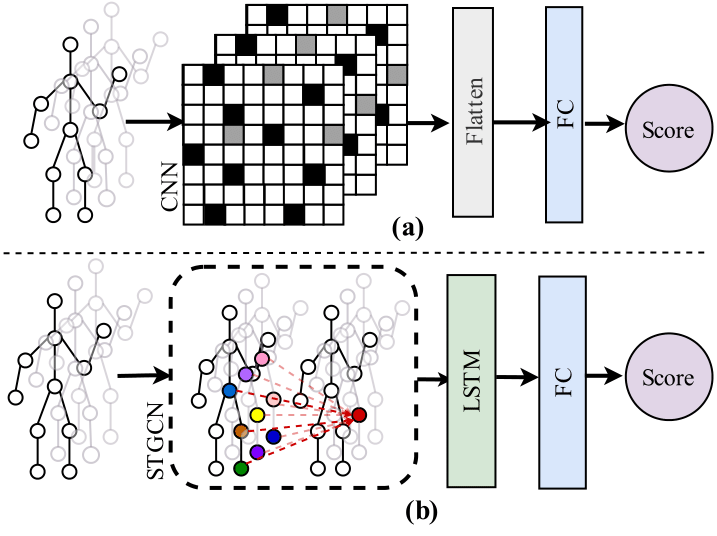
- Developed an RGB-D sensing framework using Kinect v2 to acquire spatio-temporal 3D human skeletal joint data for exercise assessment
Methods / Stack
- ROS(Noetic) Navigation Stack (planning, localization, obstacle avoidance)
- Sensor stack: LiDAR
- RGB-D–based skeletal joint data were processed using an ST-GCN to predict exercise performance scores
Media