3D Mapping Using Graph Convolutional Neural Networks for Autonomous Navigation
Learning-based 3D environment representation and mapping for autonomous navigation using graph neural networks.
Overview
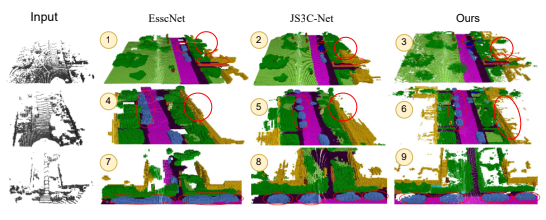
This project was my undergraduate thesis, focused on developing a learning-based framework for 3D mapping and environment representation to support autonomous robot navigation. The work explored how Graph Convolutional Neural Networks (GCNs) can be used to model spatial relationships in 3D environments more effectively than traditional grid-based representations.
Objective
- To design a graph-based representation of 3D environments suitable for autonomous navigation
- To apply Graph Convolutional Neural Networks for learning spatial and topological relationships
- To evaluate the effectiveness of graph-based mapping compared to conventional approaches
My Role
- Designed the overall mapping and learning framework
- Constructed graph representations from 3D spatial data
- Implemented and trained Graph Convolutional Neural Network models
- Conducted experiments and performance analysis for navigation-related tasks
- Authored the full undergraduate dissertation
Methodology
- Converted 3D spatial data into graph structures
- Applied GCN layers to learn relational features
- Evaluated learned representations for navigation and mapping quality
Media
Links
- Dissertation Report: PDF